Solar lights offer a clean, self-sufficient, and low-maintenance solution for outdoor and even indoor lighting. They harness energy from the sun, store it during the day, and automatically convert it into illumination at night—without the need for wires or external electricity. But how exactly does this process work?
In this article, we explore the technology behind solar lights, the key components involved, and what determines their performance.
The Basic Working Principle
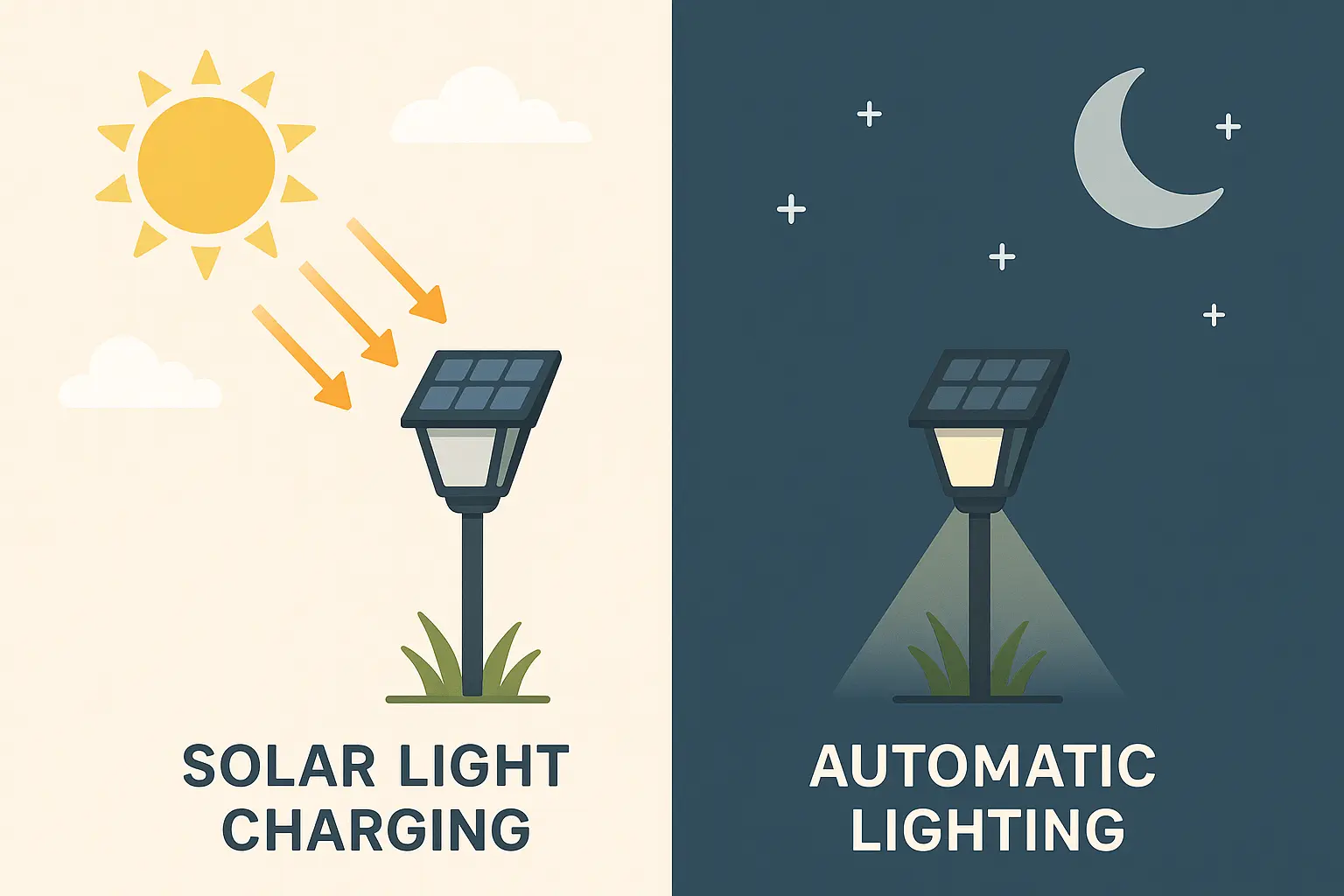
At the core, solar lights operate on the photovoltaic effect—the ability of solar cells to convert sunlight into electrical energy. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Daytime: Solar panels absorb sunlight and convert it into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Energy Storage: The DC electricity is stored in a built-in rechargeable battery.
- Nighttime Activation: A photoresistor (light sensor) detects darkness and automatically triggers the LED light to turn on.
- Battery Power Usage: The stored energy powers the light throughout the night until daylight returns.
This cycle repeats daily, with minimal user intervention.
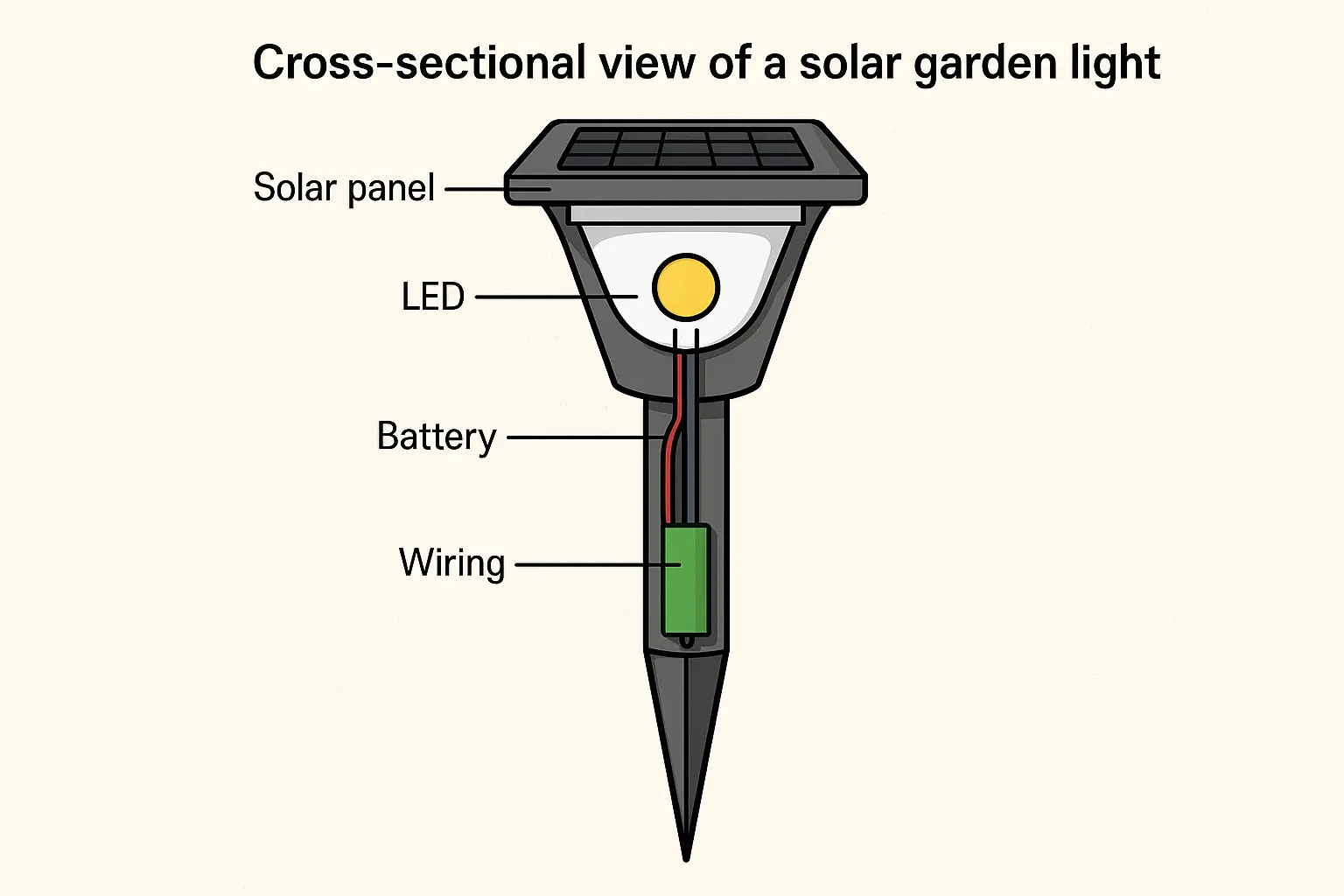
Key Components of Solar Lights
Each solar light is composed of several essential parts that work together to ensure functionality and performance:
1. Solar Panel
The panel captures sunlight and initiates the energy conversion process. There are two common types:
- Monocrystalline: Higher efficiency, better performance in low light, but typically more expensive.
- Polycrystalline: More cost-effective, slightly less efficient, better suited for full-sun environments.
2. Rechargeable Battery
Stores the electricity generated by the solar panel. Battery quality directly affects how long the light can operate at night.
- NiMH (Nickel-Metal Hydride): Stable and widely used in entry-level models.
- Lithium-ion: Longer lifespan, higher capacity, and faster charging—ideal for high-output or smart solar lights.
3. Charge Controller (Optional in Basic Units)
Regulates voltage and current to prevent overcharging or discharging the battery. Found in more advanced solar systems.
4. Light Sensor (Photocell)
Automatically detects changes in ambient light and switches the LED on at dusk and off at dawn.
5. LED Bulb
Light-Emitting Diodes are highly efficient and consume minimal power while offering bright, long-lasting illumination.
6. Housing and Optics
The casing protects all components and often includes design elements to diffuse or direct light. Weatherproof materials and IP ratings are crucial for durability.
Charging and Lighting Cycle
| Time of Day | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Morning | Solar panel begins absorbing sunlight |
| Midday | Peak energy production and battery charging |
| Late Afternoon | Battery reaches full or partial charge |
| Dusk | Photoresistor detects low light and activates the LED |
| Night | LED runs off stored battery power |
| Sunrise | LED turns off; cycle restarts |
Factors That Affect Performance
Several external factors influence how well solar lights function:
- Sunlight Exposure: Direct sunlight for at least 6–8 hours daily is essential for full charging.
- Panel Cleanliness: Dust, snow, or debris can reduce charging efficiency.
- Temperature and Weather: Extreme cold or overcast days can affect battery performance.
- Installation Angle: Panels tilted toward the sun’s path will absorb more energy.
- Battery Age: Older batteries may hold less charge and should be replaced every 1–2 years.
Advantages of Solar Lighting Systems
- Energy Efficient: No utility electricity required—completely solar-powered.
- Low Maintenance: Minimal upkeep needed after installation.
- Environmentally Friendly: No emissions, wiring, or fossil fuel usage.
- Easy Installation: No trenching or electrical knowledge required.
- Automatic Operation: Turns on and off with natural light conditions.
Limitations and Considerations
- Reliant on Sunlight: Limited effectiveness in shaded areas or cloudy climates.
- Battery Replacement Required: Rechargeable batteries degrade over time.
- Initial Investment: High-quality units cost more upfront, but save in the long term.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how solar lights function empowers users to make smarter purchasing decisions and maximize their long-term performance. With clean energy technology, reliable automation, and simple installation, solar lights represent a practical choice for homeowners, facility managers, and sustainability-focused businesses alike.

Leave a Reply